LCM (Least Common Multiple) for Grade 4
This is a comprehensive lesson plan for teaching LCM or Least Common Multiple to grade 4 students. The lesson is designed to make the concepts easy and engage students with activities like quizzes, practice questions and worksheets.
Teachers can use this guide as a reference for delivering the concepts to students and engaging them in the classroom with the various questions and examples given on this page.
For parents, there are 12 downloadable practice worksheets that they can use for their kids.
In this blog, you will learn
- LCM - it's definition and how to find it with examples
- LCM by prime factorization method with examples
- LCM by division method with examples
What is LCM?
LCM means Least Common Multiple. It is the smallest number that happens to be a common multiple of two or more numbers.
How to find LCM?
- Write the multiples of the numbers.
- Find the common multiples.
- Choose the least common multiple.
Example 1: Find the LCM of 4 and 5
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28…
- Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30…
- The smallest common multiple is 20. Hence LCM(4, 5) = 20.
Example 2: Determine the LCM of 6 and 8
- Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36…
- Multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40…
The smallest or least common multiple is 24. Therefore, LCM(6, 8) = 24.
LCM of 2, 3 and 4:
- Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14...
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15...
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16...
- The smallest or least common multiple is 12. Therefore, LCM(2, 3, 4) = 12.
LCM of 4 and 5:
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20...
- Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20...
- The smallest or least common multiple is 20. Therefore, LCM(4, 5) = 20.
LCM of 4 and 6:
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20...
- Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24...
- The smallest or least common multiple is 12. Therefore, LCM(4, 6) = 12.
Know how to find the LCM of 12, 15 and 21 here.
LCM by Prime Factorization method
Prime factorization is breaking a number into prime factors, which are the smallest numbers that multiply to give the original number.
Example: Find the LCM of 12 and 15 by using the Prime Factorization method
Step 1: Prime factorization of 12: 12 = 2 × 2 × 3
Step 2: Prime factorization of 15: 15 = 3 × 5
Take all the prime factors, using the highest powers of each factor: 2, 2, 3, 5
Multiply the factors: LCM = 2 x 2 x 3 x 5 = 60
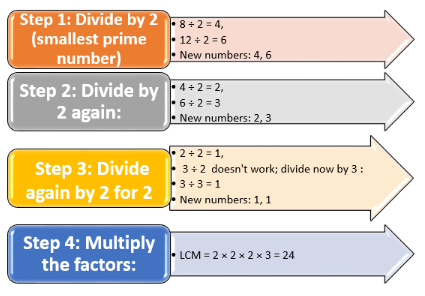
LCM by Division Method
This method involves dividing the numbers by their common factors until no common factors are left.
Example: Find the LCM of 8 and 12 using the Division Method
- Step 1: Divide by 2 (smallest prime number):
8 ÷ 2 = 4, 12 ÷ 2 = 6
New numbers: 4, 6 - Step 2: Divide by 2 again:
4 ÷ 2 = 2, 6 ÷ 2 = 3
New numbers: 2, 3 - Step 3: Divide again by 2 for 2 :
2 ÷ 2 = 1, 3 ÷ 2 doesn't work; divide now by 3 :
3 ÷ 3 = 1
New numbers: 1, 1
Multiply the factors: LCM = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 1 = 24
Fun Fact
Did you know that the LCM can help you when you are scheduling events?
For example, if two events happen at different times (like one every 4 days and another every 6 days), the LCM will tell you when both events will happen on the same day again. So, the LCM of 4 and 6 is 12, which means the two events will happen together every 12 days.
Orchid's learning material
Click the button to download the e-book
FAQs
1. What is LCM for Grade 4?
LCM stands for Least Common Multiple, which is the smallest number that is exactly divisible by two or more given numbers. For example, the LCM of 4 and 6 is 12 because 12 is the smallest number that both 4 & 6 divide evenly into.
2. How to find the LCM of 1 to 10?
-
To find the LCM of the numbers 1 through 10, list out the prime factors of each number & take the highest powers of each prime.
-
The LCM of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 is 2520.
3. What is the LCM of 24 and 36?
The LCM of 24 & 36 is 72.
You can find it by listing their multiples or using prime factorization:
-
Prime factorization of 24 = 2³ × 3
-
Prime factorization of 36 = 2² × 3²
-
LCM = 2³ × 3² = 72
4. What is the LCM rule?
The LCM rule states that the least common multiple is the smallest number, which is a multiple of each number in a given set.
Things you have learned!
- What is LCM?
- How to find LCM using the Prime Factorization Method and Division Method.











