Profit and Loss
Introduction To Profit And Loss For Class 5
Here, we will study some interesting and helpful ideas about selling and purchasing items. You'll be introduced to what profit and loss are, and how to calculate the cost price, selling price, and marked price of products. We'll also discover what discounts are when we purchase an item for less. Don't worry—we'll make use of simple formulas to assist you in solving these problems. This subject has a Table of Contents to indicate to you what we are going to learn, solved examples to better enable you to understand, practice questions to attempt on your own, and FAQs to respond to your frequent questions. Let's begin and enjoy learning!
In our daily life, the knowledge of profit and loss is essential. Here students learn how to calculate the selling price of a product and how to calculate the cost price of a product.
Let’s learn more about profit and loss.
What is Profit and Loss?
In our daily life, we buy and sell many things. When we sell something, we may gain money (profit) or lose money (loss). This is called Profit and Loss.
Concepts
Definition of Profit:
Profit is the money made by an individual or company when they sell something for a price higher than they paid for it or created it.
In simple terms, profit occurs when the price of selling is higher than the price of cost.
Definition of Loss:
Loss is the quantity of money that an individual or company loses when they sell a product or thing for lower than what they paid or created it for.
That is, loss occurs when the cost price is greater than the selling price.
Cost Price
Cost Price, abbreviated as C.P., is the basic price of an article.
It is the price paid to purchase or produce a product in order to sell it.
In other words:
Cost Price is the money you pay to acquire something.
-
It is the initial amount at which a product is offered.
-
It may involve the cost of purchase, shipping, duty, and other expenses incurred to prepare the item for sale.
-
It is employed in determining Profit or Loss upon selling the item.
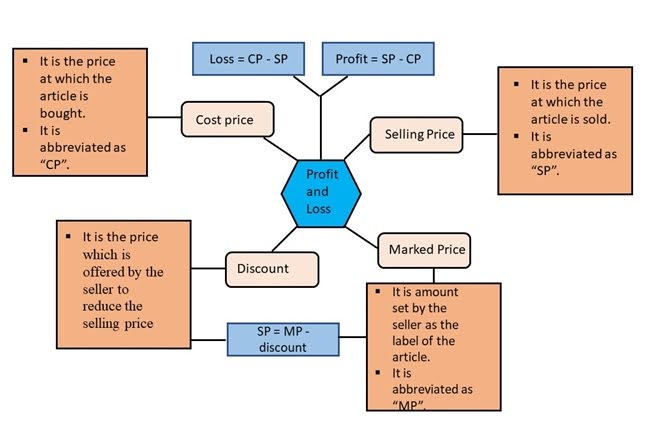
Selling Price
Selling Price, abbreviated as S.P., is the price given when a commodity is sold to an individual.
In simple terms:
Selling Price is money you receive when selling something.
-
It is the last price at which a good is sold.
-
It can be equal to, greater than, or lesser than the Cost Price.
-
It assists us in determining if we earned a profit or a loss.
Marked Price
Marked Price, abbreviated as M.P., is the price marked on the label or tag of an item prior to providing a discount.
In simple terms:
Marked Price is the price indicated on the product, normally prior to offering a discount.
-
It is also referred to as the List Price or Label Price.
-
This is the price fixed by the shopkeeper or seller.
-
The Selling Price can actually be lower than the Marked Price in case of a discount.
Discount
The amount which is offered by the seller to reduce the selling price is called the discount.
While selling a product three conditions may arise:
-
Cost Price is less than selling price, i.e., C.P < S.P
-
Cost price is more than the selling price, i.e., C.P > S.P
-
Cost price is equal to the selling price, i.e., C.P = S.P.
Based on this condition the seller either makes a profit or a loss.
Formula and Examples For Class 5:
1. The formula to calculate the profit is,
“Profit = Cost price – Selling Price”.
Solved example: The cost price of an article is Rs 74 and the selling price is Rs 86 each. Find the profit made in selling 23 such articles.
Solution:
Step 1: The cost price of an article is Rs 74.
Multiply 74 by 23 to get the cost price of 23 articles.
74 × 23 = 1,702
Step 2: The selling price of an article is Rs 86.
Multiply 86 by 23 to get the selling price of 23 articles.
86 × 23 = 1,978
Step 3: Subtract 1,702 from 1,978 to get the profit.
Profit = Cost price – Selling Price
1,978 – 1,702 = 276
Therefore, the profit made in selling 23 articles is Rs 276.
2. The formula to calculate loss is
“Loss = Cost Price – Selling Price”.
Solved example: Bhavan bought 20 boxes of gifts for Rs 1,642. He sold each box for Rs 58. Find the loss or profit made by him.
Solution:
Step 1: The selling price of 1 box = Rs 58.
Number of boxes = 20
Total selling price = 58 × 20
= 1,160
Step 2: The cost price of 20 boxes = Rs 1,642.
The selling price of 20 boxes = Rs 1,160
Loss = Cost Price – Selling Price
Loss = 1,642 – 1,160
= 482
3. The formula for the profit and loss percentage is:
Profit percentage (P%) = (Profit /Cost Price) x 100
Loss percentage (L%) = (Loss / Cost price) x 100
How to Calculate the Selling Price of a Product?
-
If a seller provides a discount on the marked price, then the selling price is calculated as “Selling Price = Marked Price – Discount”.
-
If the cost price and the profit are given then the selling price is calculated as “Selling Price = Cost Price + Profit”.
-
If the cost price and the loss is given then the selling price is calculated as “Selling Price = Cost Price – Loss”.
1. Solved Example: The marked price of the washing machine was Rs 29,780. The shopkeeper offers a discount of Rs 5645 as a “Diwali Sale”. Calculate the selling price of the washing machine.
Solution:
Marked Price = Rs 29,780.
Discount = 5645
Selling Price = 29,780 – 5645
= 24,135
2. Solved Example: The cost price of the articles is Rs 24,906. The man sold the articles at a loss of Rs 904. Find the selling price.
Solution:
Coat Price of an article = Rs 24,906.
Loss = 904
Selling price = Rs 24,906 – 904
= Rs 24,002
How to Calculate the Cost Price of a Product?
-
If an additional amount is spent on repairing or modifying an article then the total cost price of an article is equal to the sum of the price at which the article is bought and the additional price which is spent on the article”.
-
If the selling price and the profit are given then the cost price is calculated as “Cost Price = Selling Price – Profit”.
-
If the selling price and the loss are given then the cost price is calculated as “Cost Price = Selling Price + Loss”.
Solved Example: A man bought a motorbike for Rs 25,000. He spent Rs 3500 on paperwork, and Rs 7000 for changing the motor parts. At what price should he sell the motorbike to make a profit of Rs 3000.
Solution:
Step 1: Amount spent on paperwork = 3500
Amount spent on motor parts = Rs 7000
Total additional cost = Rs 3500 + Rs 7000 = Rs 10,500
Step 2: Cost price of the motorbike = Rs 25,000.
Additional cost = Rs 10,500
Total cost price = Rs 25,000 + 10,500 = Rs 35,500
Step 3: Total cost price = Rs 35,500
Profit = Rs 3000
Selling Price = Rs 35,500 + Rs 3000
= Rs 38,500
Profit and Loss Questions for Class 5:
Word Problems
-
Meena bought 15 storybooks for ₹90 each and sold them all for ₹100 each.
What is her total profit? -
A shopkeeper sold a fan for ₹2,400 after giving a discount of ₹600.
What was the marked price of the fan?
Profit & Loss Percentages
-
A bag was sold for ₹900 with a profit of ₹100.
Find the profit percentage. -
A laptop was sold for ₹18,000 at a loss of ₹2,000.
What is the loss percentage?
Application of Formulas
-
Selling Price = ₹750, Profit = ₹150.
Find the Cost Price. -
Selling Price = ₹420, Loss = ₹80.
Find the Cost Price. -
Cost Price = ₹1,000, Profit % = 25%.
What is the Selling Price?
FAQs
1. Why is it important to learn about profit and loss?
Answer: Learning about profit and loss helps us understand how to manage money. It teaches us whether we are gaining or losing money when we buy and sell things. This knowledge is useful in daily life and in running a business.
2. What is the difference between cost price and selling price?
Answer:
-
Cost Price (C.P.) is the amount paid to buy or make an item.
-
Selling Price (S.P.) is the amount for which the item is sold.
If the selling price is more than the cost price, there is a profit. If it is less, there is a loss.
Misconceptions About EMI:
Misconception 1: Profit is always a good thing, and loss is always bad.
Reality:
While profit usually means earning more money, it’s not always good if it involves cheating or overpricing. Similarly, a loss isn’t always bad—sometimes items are sold at a loss to clear old stock or attract more customers.
Misconception 2: Profit = Selling Price – Marked Price
Reality:
Profit is calculated as Profit = Selling Price – Cost Price, not the marked price. The marked price is often higher and only used to calculate discounts, not profit or loss.
Misconception 3: If there is a discount, the seller always faces a loss.
Reality:
Giving a discount does not always result in a loss. If the discounted selling price is still higher than the cost price, the seller still makes a profit.
Misconception 4: Loss means losing all the money spent.
Reality:
A loss means that the selling price is less than the cost price, but it doesn’t mean the entire amount is lost. It’s just the difference between cost price and selling price.
Misconception 5: Profit or loss is always calculated on the selling price.
Reality:
Profit and loss percentages are always calculated based on the cost price, not the selling price.
Example:
Profit % = (Profit ÷ Cost Price) × 100











