Types of Fraction
Introduction
Fractions are found everywhere, from dividing a pizza to splitting a chocolate bar. Knowing various types of fraction helps us in understanding advanced math concepts like ratios, proportion and algebra. Fractions allow us to represent parts of a whole, to solve sharing problems and do many real-life calculations. In this blog, we will explain what fraction is, different types of fraction, and their representation using clear examples that will help make learning fun and easy for you. Whether you're beginning to learn fraction or need a refresher on the basics, this guide is for you. We will start with what a fraction means and what are the different types of fraction in maths.
Table Of Content
- What Is a Fraction?
- Types of Fraction
- Proper Fractions
- Improper Fractions
- Mixed Fractions
- Fraction Examples in Real Life
- Simplifying Fractions
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Practice Questions
- Conclusion
- FAQs on Types of Fraction
What Is a Fraction?
Before learning about different type of fraction we need to understand what is a fraction. A fraction is a way to show a part of a whole. It displays how many equal parts of a thing are taken from the total number of parts, which is the whole. It is written with two numbers: one on the top and one at the bottom, separated by a line. This line is called the fraction bar.
The number on top is called the numerator, and the number at the bottom is the denominator.
For example:
3/4 → 3 is the numerator (part), 4 is the denominator (whole)
If a cake is cut into 4 equal parts and you eat 3, then you've eaten 3 out of 4, or 3/4.
This basic idea forms the base of the definition of fraction and leads us to understand the kinds of fraction in more detail.
Types of Fraction
Out of all the mathematical concepts that you study in primary and middle school, learning fractions and their types is very important. Let's look at the different types of fractions.
There are mainly three types of fraction in basic mathematics:
-
Proper Fractions
-
Improper Fractions
-
Mixed Fractions
Let’s learn what each type of fraction with examples.
Proper Fractions
A fraction is known as a proper fraction when the numerator is less than the denominator.

Examples:
-
1/2
-
3/4
-
5/9
In these, the part is smaller than the whole. That’s why they are called proper fractions.
Improper Fractions
A fraction is called an improper fraction when the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator.
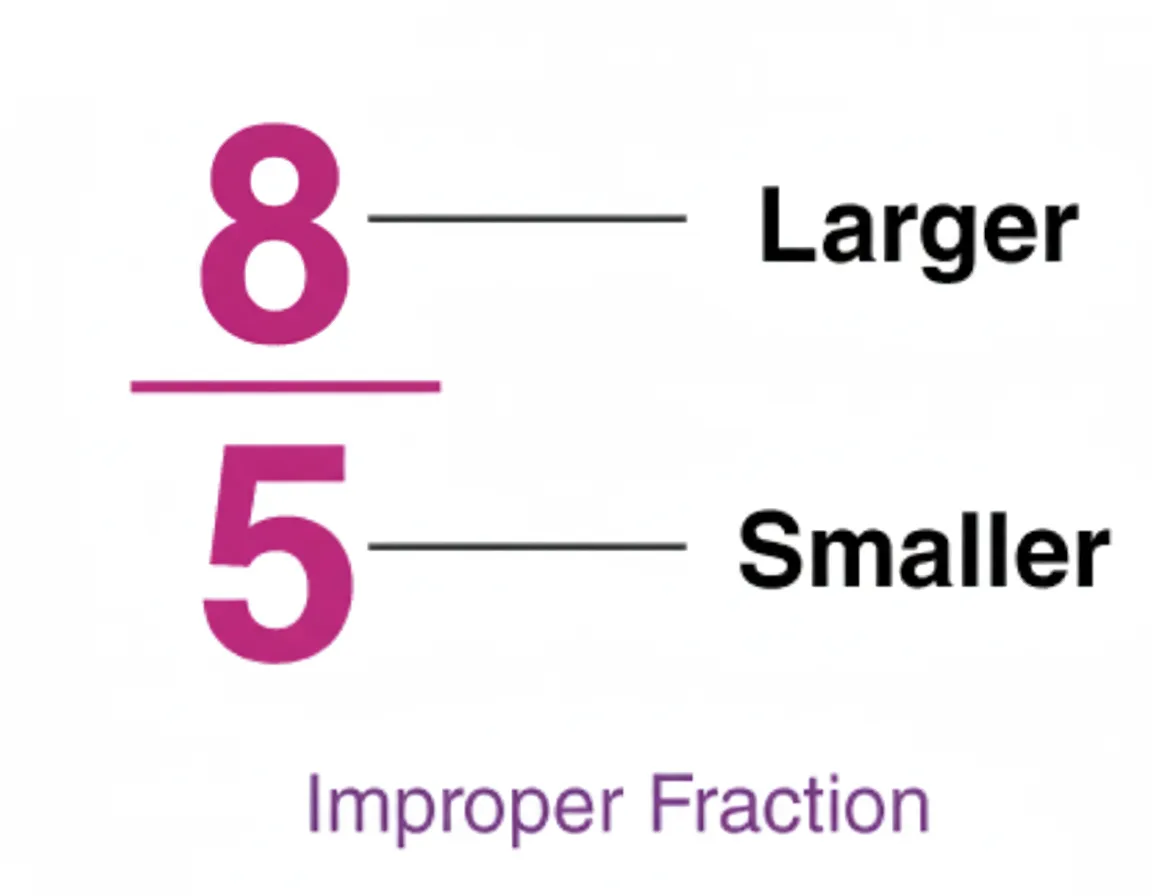
Examples:
-
5/4
-
9/7
-
12/12
These fractions show that you have more than one whole or exactly one.
Mixed Fractions
A mixed fraction is a combination of a whole number and a proper fraction.

Examples:
-
$1\tfrac{2}{2}$
-
$2\tfrac{3}{4}$
-
$5\tfrac{2}{5}$
These are used when we want to show a number greater than 1 more clearly.
In addition to the main three, there are other types of fraction based on how they look and behave.
Like Fractions
Fractions with the same denominator are like fractions.
For Examples:
- 1/5
- 2/5
- 4/5
Unlike Fractions
Fractions with different denominators are unlike fractions.
For Examples:
- 1/3,
- 1/4,
- 1/6
Equivalent Fractions
Fractions that look different but mean the same.
Example: 1/2 = 2/4 = 4/8
Understanding all these types of fraction will helps students identify relationships between different values.
Why are Fraction Important?
Fractions are useful in many real life situations such as for slicing & distributing or sharing food like cake, pizza, drink, etc. They are useful in dividing money among people, measuring ingredients while cooking, understanding discounts/offers and so on. Knowing the types of fraction helps you solve problems faster and more accurately.
Let’s look at a few real life fraction examples to make learning easier.
-
If a pizza is divided into 8 slices and you eat 3, then you’ve eaten 3/8 of the pizza.
-
If a water bottle holds 1 liter and you drink half of it, you’ve consumed 1/2 liter.
-
If a class has 20 students and 5 are absent, then 5/20 or 1/4 of the class is missing.
These daily examples help children understand the concept better.
Comparing Fractions
To compare fractions, you need to check:
-
If the denominators are the same, simply compare the numerators.
-
If they are different, convert them to like fractions (same denominator).
Example:
Which is greater: 3/5 or 2/3?
Convert both to a common denominator →
3/5 = 9/15
2/3 = 10/15
So, 2/3 is greater.
Converting Fractions
You can also change between different types of fraction:
Improper to Mixed
Example:
7/4 = 1 3/4
(Divide 7 by 4: quotient is 1, remainder is 3)
Mixed to Improper
Example:
2 1/3 = (2×3 + 1)/3 = 7/3
Knowing these conversions makes math easier and quicker.
Simplifying Fractions
Sometimes, fractions can be made simpler without changing their value.
Example:
4/8 → divide both by 4 → becomes 1/2
So, 4/8 and 1/2 are equivalent fractions.
This step is called simplification or reducing fractions.
Adding and Subtracting Fractions
The process of addition of fractions is similar to the process of subtraction. To add or subtract fractions:
-
Make the denominators the same (find a common denominator)
-
Then add or subtract the numerators
Example:
1/4 + 2/4 = (1+2)/4 = 3/4
5/6 – 1/6 = 4/6 → simplify → 2/3
This method works for all kinds of fraction with like or unlike denominators.
Multiplying and Dividing Fractions
Multiplying:
Multiply the numerators and the denominators.
Example:
2/3 × 3/4 = 6/12 → simplify → 1/2
Dividing:
Flip the second fraction and multiply.
Example:
3/5 ÷ 2/7 = 3/5 × 7/2 = 21/10
This is useful in both school math and in solving word problems.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
-
Mixing up the numerator and the denominator
-
Forgetting to simplify answers
-
Adding fractions without a common denominator
-
Confusing improper fractions and mixed numbers
Learning the types of fraction correctly helps you avoid these errors.
Practice Questions
-
Write whether these are proper, improper, or mixed:
-
4/9
-
7/3
-
2 1/2
-
Convert to improper fractions:
-
3 2/3
-
1 1/4
-
Simplify:
-
6/12
-
15/25
-
Solve:
-
1/2 + 3/4 = ?
-
5/6 – 2/3 = ?
These fraction questions help you master all types of fraction with ease.
Conclusion
Fractions are an essential part of learning mathematics. By understanding the types of fraction, students gain the tools to solve many problems in everyday life and exams. Whether it’s sharing a cake, reading a recipe, or solving a math puzzle, knowing the kinds of fraction makes everything simpler.
This blog has explained the fraction definition and examples in a fun and easy way. From proper to mixed fractions, from simplifying to solving, everything becomes clearer with the right practice. Keep exploring, keep learning, and fractions will no longer feel tricky.
FAQs on Types of Fractions
1. What are the 7 types of fractions?
Answer: The 7 common types of fractions are:
-
Proper Fractions
-
Improper Fractions
-
Mixed Fractions
-
Like Fractions
-
Unlike Fractions
-
Equivalent Fractions
-
Unit Fractions
2. What are mixed fractions?
Answer: A mixed fraction is a combination of a whole number and a proper fraction. for example 172
3. Explain improper fractions with examples?
Answer: An improper fraction is a fraction that has a numerator bigger than its denominators. Some examples of improper fractions are:
- 7/4
- 8/7
- 12/5
4. What are the 12 types of fractions with examples?
Answer: Here are 12 types of fractions with examples:
-
Proper Fraction – 2/3
-
Improper Fraction – 7/4
-
Mixed Fraction – 1½
-
Like Fractions – 2/5 and 3/5
-
Unlike Fractions – 1/2 and 2/3
-
Equivalent Fractions – 1/2 = 2/4
-
Unit Fraction – 1/4
-
Decimal Fraction – 0.75
-
Vulgar Fraction – 3/7
-
Positive Fraction – 4/5
-
Negative Fraction – -3/8
-
Complex Fraction – (3/4) ÷ (2/5)
5. What is fraction in Class 7?
Ans: In Class 7, a fraction is defined as a number that represents part of a whole. It is written as a/b, where "a" is the numerator and "b" is the denominator. Students also learn operations like , subtraction of fractions, multiplication, and division with fractions.
Discover more fun ways to learn math and practice fractions at Orchids The International School.
Related Links
CBSE Schools In Popular Cities
- CBSE Schools in Bangalore
- CBSE Schools in Mumbai
- CBSE Schools in Pune
- CBSE Schools in Hyderabad
- CBSE Schools in Chennai
- CBSE Schools in Gurgaon
- CBSE Schools in Kolkata
- CBSE Schools in Indore
- CBSE Schools in Sonipat
- CBSE Schools in Delhi
- CBSE Schools in Rohtak
- CBSE Schools in Bhopal
- CBSE Schools in Aurangabad
- CBSE Schools in Jabalpur
- CBSE Schools in Jaipur
- CBSE Schools in Jodhpur
- CBSE Schools in Nagpur
- CBSE Schools in Ahmednagar
- CBSE School In Tumkur













