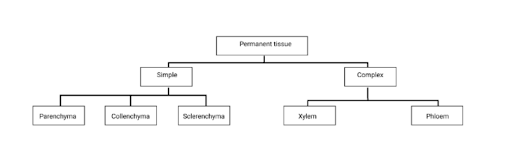
The types of simple tissues are as follows:
➢ Parenchyma
➢ Collenchyma
➢ Sclerenchyma
Tissues are groups of cells that work together to perform specific functions in the body. They play a crucial role in forming organs and systems, contributing to everything from movement to protection. There are four main types of tissues: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous, each with unique structures and functions. Understanding tissues is essential for studying biology and medicine, as they form the foundation of all living organisms.
The NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 6 – Tissues are tailored to help the students master the concepts that are key to success in their classrooms. The solutions given in the PDF are developed by experts and correlate with the CBSE syllabus of 2025-2026. These solutions provide thorough explanations with a step-by-step approach to solving problems. Students can easily get a hold of the subject and learn the basics with a deeper understanding. Additionally, they can practice better, be confident, and perform well in their examinations with the support of this PDF.
Download PDF
Students can access the NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 6 – Tissues. Curated by experts according to the CBSE syllabus for 2025–2026, these step-by-step solutions make Science much easier to understand and learn for the students. These solutions can be used in practice by students to attain skills in solving problems, reinforce important learning objectives, and be well-prepared for tests.
Name the types of simple tissues.
The types of simple tissues are as follows:
➢ Parenchyma
➢ Collenchyma
➢ Sclerenchyma
Where is apical meristem found?
In plants, apical meristem is typically found at:
• The tip of the shoot
• Root of the plant
Which tissue makes up the husk of a coconut?
The sclerenchymatous tissue, which is a type of permanent tissue makes up the husk of the coconut. These tissues causes the plant to become stiff and hard. The cells of this tissue are dead and their cell walls are thickened because of the presence of lignin.
What are the constituents of phloem?
The phloem constitutes of the following four elements, they are:
➢ Sieve tube
➢ Companion cells
➢ Phloem parenchyma
➢ Phloem fibres
Name the tissue responsible for movement of our body.
Two tissues jointly are responsible for the movement of our body, namely:
➢ Muscular tissue
➢ Nervous tissue
Give three features of cardiac muscles.
Cardiac muscles are specialized tissues that are evolved to pump blood throughout the body.
The following are the features of cardiac muscles:
➢ They are cylindrical in shape.
➢ Striated muscle fibers.
➢ They are uninucleated and branched.
➢ These muscles are involuntary in nature.
What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Areolar tissues are typically observed in animals. They are connective tissues and are found in between skin and muscles. They are also located around blood vessels and nerves, and are present in the bone marrow. The space inside the organs is filled with these tissues. They support the delicate internal organs and assist in tissue repair in case of damage.
Define the term ’tissue’.
A tissue is defined as a cluster of cells, which are similar in structure and work together to perform a particular function.
How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
The xylem tissue is made up of four main elements, namely:
➢ Vessels
➢ Tracheids
➢ Xylem fibres
➢ Xylem parenchyma
Identify the type of tissue in the following:
Skin, bark of tree, bone, lining of kidney tubule, vascular bundle.
➢ Skin: Stratified squamous epithelial tissue
➢ Bark of tree: Protective tissue and cork
➢ Bone: Connective tissue
➢ Lining of kidney tubule: Cuboidal epithelial tissue
➢ Vascular bundle: Conducting tissue (xylem and phloem), complex permanent tissue
Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
The parenchyma is found in:
• The pith of stems and roots
• When parenchyma contains chlorophyll it is called a chlorenchyma. It is found in green leaves
• Parenchyma found in aquatic plants has large air cavities which enables them to float, and are hence called aerenchyma.
What is the role of epidermis in plants?
The epidermis in plants forms an uninterrupted and continuous layer that has no intercellular spaces. It provides protection.
How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
Cork cells are dead. The arrangement of cells is so dense, that there is no intercellular space. Deposition of suberin is observed on the walls of the cells that make them impervious to water and gases.
What are the functions of the stomata?
Stomata are the tiny pores present on the outer layer of the cells, the epidermis. Stomata bring about the exchange of gases and transpiration.
What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle?
The cardiac muscles are branched and cylindrical. They are uninucleated and are involuntary in nature. The cardiac muscles bring about a rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout one’s lifetime.
What is a tissue?
A tissue is defined as a cluster of cells, which are similar in structure and work together to perform a particular function.
What is the utility of tissues in multicellular organisms?
The use of tissues in multicellular organisms is to provide structural and mechanical strength as well as to allow division of labour.
How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
The following are the differences:
|
Simple tissues |
Complex tissues |
|
They are made up of a single type of cell that performs only one common function |
They are made up of more than one kind of a cell that coordinate to perform one particular function |
Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma on the basis of their cell wall.
The following are the differences between different tissues based on cell wall:
|
Parenchyma |
Collenchyma |
Sclerenchyma |
|
Cell walls are thin and made up of cellulose |
Cell walls are thick at the edges due to the deposition of pectin |
Cell walls are thick due to the deposition of lignin |
Differentiate between striated, un-striated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site/location in the body.
The following are the differences between different types of muscles, based on their structure and location in the body.
|
Character |
Striated muscles |
Un-striated muscles |
Cardiac muscles |
|
Shape/Structure |
Long, cylindrical, non – tapering. They are un branched. |
Long and tapering. They are un-branched. |
Cylindrical and non – tapering. They are branched. |
|
Location in body |
Hands, legs and skeletal muscles |
Wall of stomach, intestine, ureter and bronchi |
Heart |
|
Dark and light bands |
Present |
Absent |
Present but less prominent |
Name the following.
(a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth.
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans.
(c) Tissue that transports food in plants.
(d) Tissue that stores fat in our body.
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix.
(f) Tissue present in the brain.
(a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth – The epithelial tissue, Squamous epithelium.
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans – Tendon
(c) Tissue that transports food in plants – Phloem
(d) Tissue that stores fat in our body – Adipose tissue
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix – Blood, it is a fluid connective tissue
(f) Tissue present in the brain – Nervous tissue
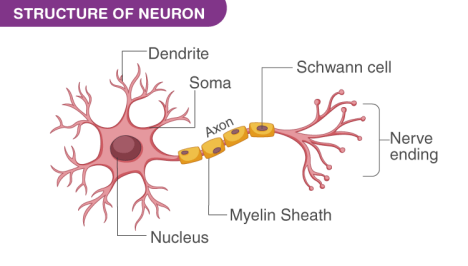
Draw a labelled diagram of a neuron.
Diagram of a neuron along with the labelling is as follows:
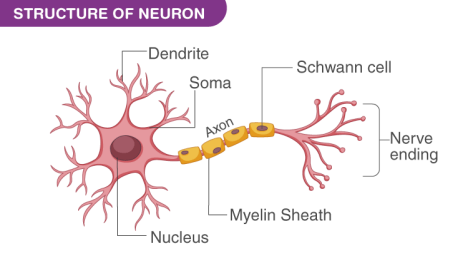
What does a neuron look like?
A neuron is a nerve cell consisting of the cell body with a nucleus and cytoplasm from which a long and thin hair-like structure emerges. Every neuron has one elongated part known as the axon, and several short and small branched structures known as dendrites. A single neuron can even be a meter long.
Complete the following chart.
The completed chart is as follows:
Show the difference between the three types of muscle fibres diagrammatically.
There are three types of muscle fibres, they are:
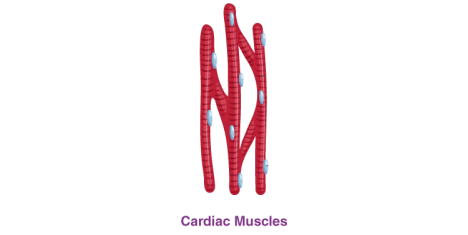
i) Cardiac muscles
• Present in the heart.
• Involuntary in nature.
• They have 1 nucleus.
• The muscle fibers are branched.
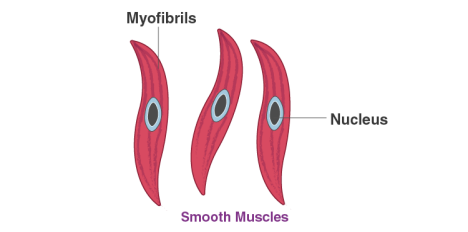
ii) Smooth muscles
• Found in lungs and alimentary canal.
• Involuntary in nature.
• They have 1 nucleus.
• They are spindle-shaped.
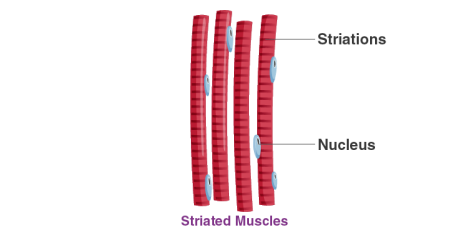
iii) Striated muscles
• They are connected with bones
• Voluntary in nature.
• They are long and cylindrical muscle fibers.
• They possess many nuclei.
• Striated muscles are unbranched.
The NCERT solution for Class 9 Chapter 6: Tissues is important as it provides a structured approach to learning, ensuring that students develop a strong understanding of foundational concepts early in their academic journey. By mastering these basics, students can build confidence and readiness for tackling more difficult concepts in their further education.
Yes, the NCERT solution for Class 9 Chapter 6: Tissues is quite useful for students in preparing for their exams. The solutions are simple, clear, and concise allowing students to understand them better. They can solve the practice questions and exercises that allow them to get exam-ready in no time.
You can get all the NCERT solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 from the official website of the Orchids International School. These solutions are tailored by subject matter experts and are very easy to understand.
Yes, students must practice all the questions provided in the NCERT solution for Class 9 Science Chapter 6: Tissues as it will help them gain a comprehensive understanding of the concept, identify their weak areas, and strengthen their preparation.
Students can utilize the NCERT solution for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 effectively by practicing the solutions regularly. Solve the exercises and practice questions given in the solution.
CBSE Schools In Popular Cities