Parts of a Seed: Explore Seed Coat, Embryo, Endosperm
A seed is the reproductive unit of angiosperms (flowering plants) capable of developing into another such plant. The following are it's parts:
|
Seed Part |
Function |
Example |
|
Seed Coat |
Protects the seed from damage & disease |
Beans, Peas |
|
Endosperm |
Stores nutrients for the growing embryo |
Coconut, Corn |
|
Embryo |
Develops into a new plant |
All flowering plants |
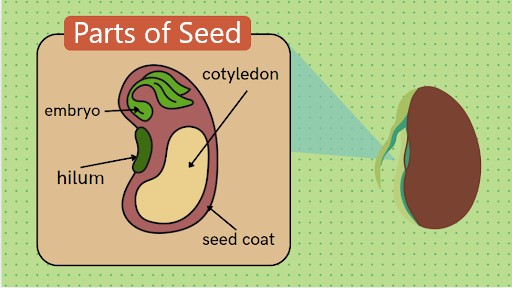
Below is the diagram of it's parts.
They have an outer shell called the seed coat that protects them from bad weather, physical damage, & germs. It has a hard seed coat.
A small scar, the hilum, shows where the seed attached to the fruit.
The embryo is the small developing plant contained within the seed.
The seed has Cotyledons, a structure that stores nutrients to feed the embryos.
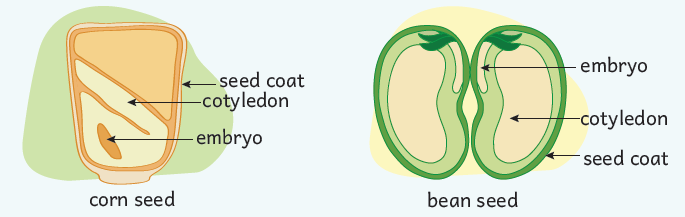
Seeds are classified as two types based on the number of cotyledons:
-
Monocotyledons (Monocots): Seeds that contain one cotyledon or seed leaf. Such as maize, rice, & wheat.
-
Dicotyledons (Dicots): These seeds have two cotyledons or seed lobes. Examples of pulse crops include gram, beans & peas.
Conclusion: Each part of a seed plays a vital role in protecting, nourishing, and developing the future plant - making seeds essential for the plant life cycle.
CBSE Schools In Popular Cities
- CBSE Schools in Bangalore
- CBSE Schools in Mumbai
- CBSE Schools in Pune
- CBSE Schools in Hyderabad
- CBSE Schools in Chennai
- CBSE Schools in Gurgaon
- CBSE Schools in Kolkata
- CBSE Schools in Indore
- CBSE Schools in Sonipat
- CBSE Schools in Delhi
- CBSE Schools in Rohtak
- CBSE Schools in Bhopal
- CBSE Schools in Aurangabad
- CBSE Schools in Jabalpur
- CBSE Schools in Jaipur
- CBSE Schools in Jodhpur
- CBSE Schools in Nagpur
- CBSE Schools in Ahmednagar
- CBSE School In Tumkur