Pollination: Definition, Process, Types
Ever wondered how plants produce seeds and fruits? Well, the plant cannot walk around like a human being. They have this rather intelligent mechanism of producing more plants. This is called pollination. It is when the pollen from a flower gets moved from one flower to another. Pollen is that powdery substance which is present on the flowers. We are going to learn more about this incredible process.
What is Pollination?
Pollination is the process that helps plants reproduce and make seeds. It happens when pollen from one flower (the male part) moves to another flower's stigma (the female part). This can happen in different ways, such as by the wind, water, or animals like bees, butterflies, and birds.
When a pollinator like a bee lands on a flower to collect nectar, some pollen sticks to its body. As the bee moves to another flower, the pollen transfers to the stigma, allowing the flower to produce seeds. This process is important for plants to grow new plants and for many fruits and vegetables to develop. Below image describes the flowchart of the progression of flower to fruits.
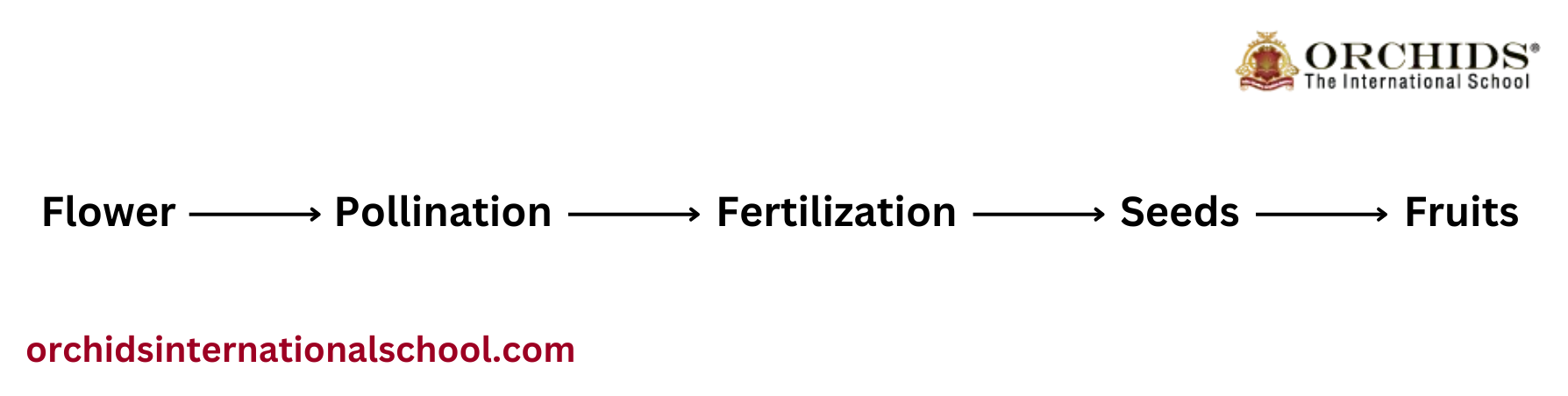
-
Flower: A flower is the reproductive part of a plant, containing both male and female parts.
-
Pollination: Pollination occurs when pollen from the male part of the flower reaches the female part, usually with the help of insects, wind, or water.
-
Fertilization: After pollination, pollen travels to the ovary to fertilize the egg cells, forming seeds.
-
Seeds: The fertilized ovary develops seeds, which contain the genetic material for a new plant and will eventually be surrounded by the fruit.
-
Fruit: The ovary also turns into a fruit, which protects the seeds inside and helps spread them to new areas for further plant growth.
What is a Flower?
A flower is the part of a plant that helps it make seeds so that new plants can grow.
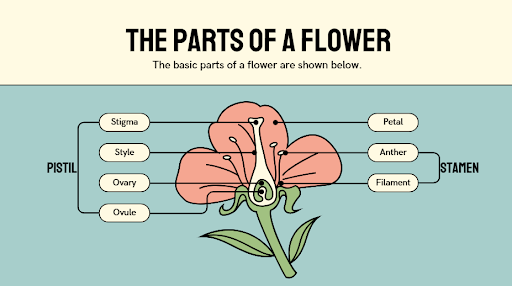
Different Parts of a Flower
1. Sepals: The small green parts that protect the flower before it blooms.
2. Petals: The flowers have bright & coloured parts to attract insects.
3. Stamens: The male reproductive parts of flowers that produce pollen. The stamen consists of the following parts:
-
Anther: A sac-like structure present on the top of the stamen. It contains powdery, fine spore-like structures called pollen grains. It is generally yellow in colour.
-
Filament or stalk: A filament or stalk is a long ,tube-like structure that holds the anther up.
4. Pistil: the female reproductive part of the flower, which produces ovules. It consists of the following parts:
-
Stigma: The sticky tip of the pistil is known as stigma. It receives pollen grains from the anther.
-
Style: It is a long, tube-like structure that connects the stigma to the basal part, which is the ovary.
-
Ovary: A bulb-like structure present at the base of the style is known as an ovary.
-
Ovules: Female egg cells present in the ovary are known as ovules. Seeds are formed from ovules.
Bisexual and Unisexual Flowers
Flowers can be divided into two types based on the parts they have: bisexual flowers & unisexual flowers.
1. Bisexual Flowers
-
What are they?
Bisexual Flowers – When a flower has both a male part (stamen) & a female part (pistil) in one flower. -
Examples: Rose, Hibiscus, Mustard.
-
Why are they special?
They contain both male & female reproductive organs in (often) the same flower, allowing them to self-pollinate (though many also can take pollen from other flowers).
2. Unisexual Flowers
-
What are they?
It is unisexual if it has only one part, either the male part (stamen) or the female part (pistil). -
Types of Unisexual Flowers:
-
Male Flowers: Only have a stamen (papaya, corn).
-
Female Flowers: Have female flowers that have only pistils (papaya, cucumber).
-
Examples: Papaya, Watermelon, and Coconut.
Key Differences
|
Feature |
Bisexual Flowers |
Unisexual Flowers |
|
Parts Present |
Both stamen & pistil |
Either stamen or pistil |
|
Examples |
Rose, Hibiscus |
Papaya, Corn |
|
Pollination Type |
Can self-pollinate |
Require cross-pollination |
Types of Pollination
Pollination is of two types: Self-pollination or Cross-pollination.
-
Self-pollination:
-
The transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower or stigma of another flower on the same plant.
-
Flowers like self-pollinated flowers: peas & cherry blossoms.
-
-
Cross-pollination:
-
Here the pollen grains are transferred to the flower of one plant from the flower of another - but still it is the same kind (a different plant)
-
Apple trees or sunflowers, for example, need pollinators like bees to transfer pollen between other plants of the same species.
-
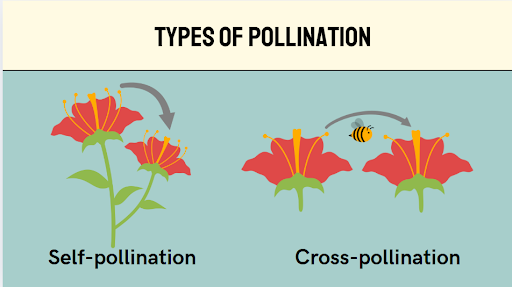
Self-pollination occurs naturally, while cross-pollination requires the assistance of pollinators.
Process of Pollination
-
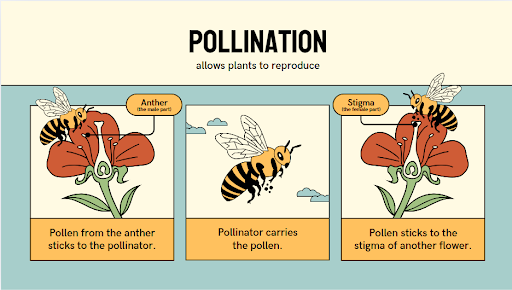
Pollination is the process by which pollen grains are transferred from the anther of one flower to the stigma of a flower.
-
The organisms that help in this transfer are called pollinators.
-
Pollinators can be monkeys, birds, & even humans.
-
Apart from living organisms, wind & water are some of the non-living pollinators.
-
Pollination is what gives fruit the seeds they carry. These seeds can sprout & turn into new sprouts.
Fun Facts About Pollination
-
Bees make some of the most active pollinators. One bee can visit thousands of flowers in a single day to gather nectar & transport pollen.
-
Flowers that rely on wind for pollination don’t need to be colorful. Flowers that do not attract insects, such as wheat & corn, have no use for bright petals.
-
Hummingbirds are unique pollinators. It has a long beak that allows it to reach the nectar deep inside flowers.
Things you have learned!
- Pollination is the process of transferring pollen from the anther (male part) to the stigma (female part) of a flower.
- Parts of a Flower - Stamen (Anther and Filament) and Pistil (Stigma, Style and Ovary), Petals, and Sepals.
- Types of Flowers - Unisexual Flowers and Bisexual Flowers.
- Types of Pollination -
Self-pollination - Pollen moves within the same flower or a different flower on the same plant.
Cross-pollination - Pollen moves between flowers of different plants of the same type.
CBSE Schools In Popular Cities
- CBSE Schools in Bangalore
- CBSE Schools in Mumbai
- CBSE Schools in Pune
- CBSE Schools in Hyderabad
- CBSE Schools in Chennai
- CBSE Schools in Gurgaon
- CBSE Schools in Kolkata
- CBSE Schools in Indore
- CBSE Schools in Sonipat
- CBSE Schools in Delhi
- CBSE Schools in Rohtak
- CBSE Schools in Bhopal
- CBSE Schools in Aurangabad
- CBSE Schools in Jabalpur
- CBSE Schools in Jaipur
- CBSE Schools in Jodhpur
- CBSE Schools in Nagpur
- CBSE Schools in Ahmednagar
- CBSE School In Tumkur













