Shadows: Definition, Characteristics, Examples
Shadows are very interesting in our daily lives. Objects are born when light from a source—for example, the Sun or a lamp—is obstructed. Lets learn more in this lesson about - what shadows are, how they form, their characteristics, and their connections to events like day and night & solar eclipses.
What are shadows?
A dark area or shape formed by an item blocking the surface of a light source is a shadow. Shadows reveal to us how light moves in straight lines & how things respond to light. Shadows cannot be if there is no light.
Formation of shadows
Shadows are formed as a result of:
-
Light is emitted from a light source, which can be the Sun or a bulb.
-
An opaque object traps the path of the light (an object that is unable to allow light).
-
The shadow falls on a surface (like a wall or the ground).
The following diagram illustrates the formation of shadows:

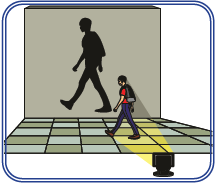
|
Light Source |
Opaque Object |
Surface |
Shadow |
|
Sun |
Tree |
Ground |
Dark Shape on the Ground |
|
Bulb |
Book |
Wall |
Dark Shape on Wall |
Want to Learn More About Shadows and How They Work?
Click here to explore the science of shadows further!
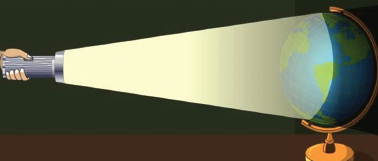
Activity: Create Your Own Shadow
At home, you might experiment with creating shadows.
-
Starting a sharp room energy lamp or flashlight.
-
Place your hand or a toy in front of the light.
-
Just pay attention to the shadow wall or floor. Move the object closer or further from the light & see how the shadow changes.
Source: Alamy
Properties of Shadows
Shadows have some interesting characteristics:
|
Property |
Explanation |
|
Shape |
Shadows take the form of the object obstructing the light. |
|
Size |
Depending on how far away the object is from the light source a shadow will change size. |
|
Color |
Shadows are typically dark because light is prevented from reaching them. |
|
Direction |
Notice that the direction of the shadow depends on where the light source is located. |
Elements influencing shadows:
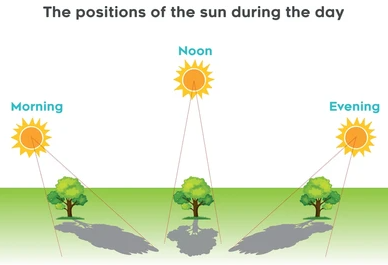
- Position of the Light Source: Since shadows are long in the morning & evening, if the main light is low; if it is directly above at noon, they are small.
- Distance Between Object and Light Source: The closer the light is to the object then the more shadow will be.")
- Type of Object: Opaque objects cast crisp shadows; translucent objects cast blurry shadows.
Experiments aimed at grasping shadows
Different sizes of the shadow
-
Hold something opaque in front of the flashlight, such as a small toy.
-
Bring the torch closer to and further away from the object & observe the change in size of the shadow.
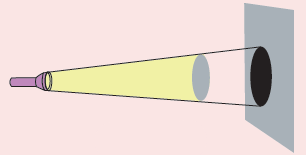
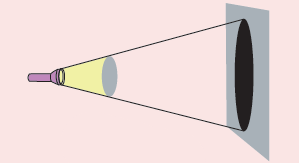
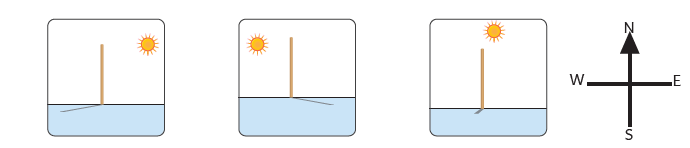
Direction of the Shadow
-
Put an object in the sun at different times (evening, mid-day & morning).
-
Notice how the angle of the shadow changes depending on where the Sun is in the sky.
The Sun is behind the causes of day and night
The rotation of the Earth on its axis gives night & day. Let's clarify how these are operated:
-
The Earth rotates every 24 hours.
-
Daytime takes place on the side of a planet facing the Sun.
-
One part of the planet that lacks light is the sun's effect.
This movement of the Earth explains why we see the Sun setting in the west and rising in the east. The direction & length of shadows are also influenced throughout the day by the moving position of the Sun.
|
Time of Day |
Position of the Sun |
Shadow Length |
Shadow Direction |
|
Morning |
Low in the Sky |
Long |
West |
|
Noon |
Directly Overhead |
Short |
Under Object |
|
Evening |
Low in the Sky |
Long |
East |
Shadow Clock
A shadow clock or sundial tells time by using the sun’s position. A stick (gnomon) casts a shadow on a marked surface, and as the sun moves, the shadow shifts, indicating the time. This ancient method of timekeeping works best on sunny days and was used before modern clocks were invented.
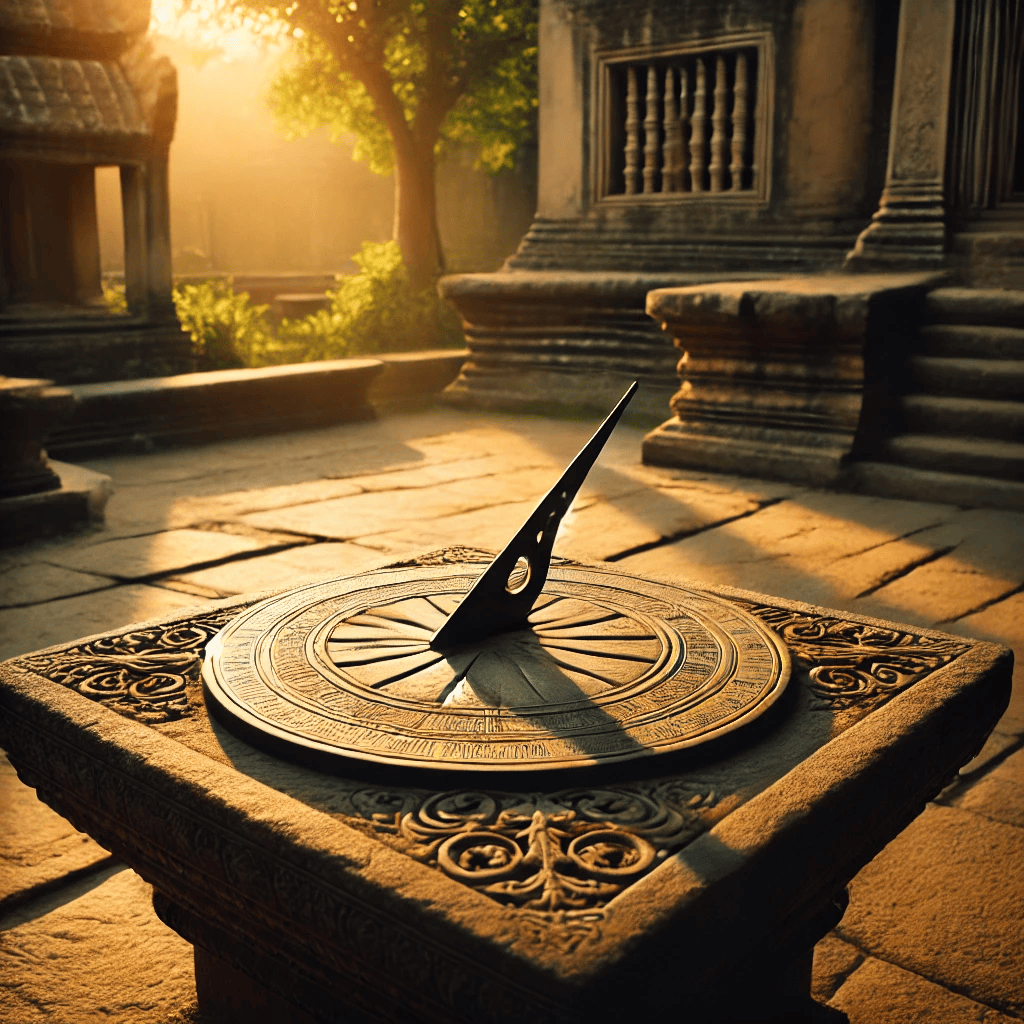

Activity:
Using a stick, you can create a basic shadow clock.
-
Erect a stick in the ground.
-
Mark the tip of its shadow every hour.
-
See how the length of the shadow all day varies & it travels.
Eclipses
One celestial body moves into the shadow of another, causing an eclipse. There are two primary forms:
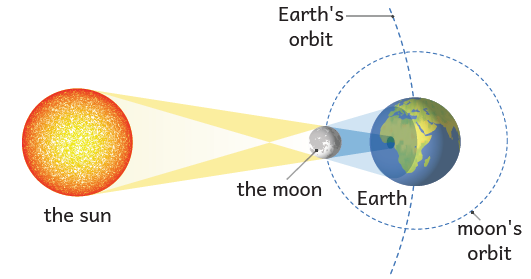
Solar Eclipse
When the Moon crosses between the Earth & the Sun. A solar eclipse happens by means of.
-
Position: Sun to Moon & Earth.
-
Types: Whole, partial, annular solar eclipses
In a solar eclipse, time-related energy patterns are driven from the sun into the Earth.
-
The day returns only during the sky.
-
Do not stare straight at a solar eclipse without proper safeguards since it may damage your eyes.
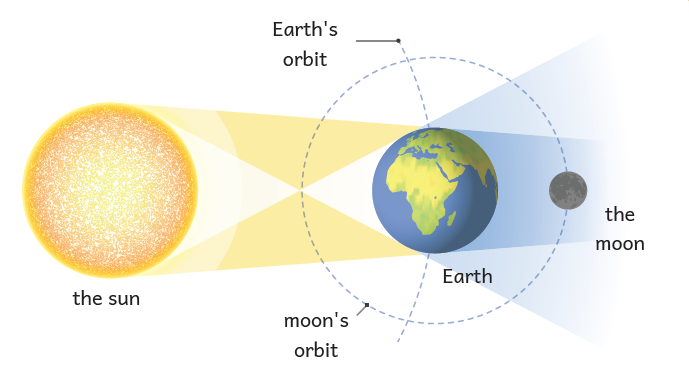
Lunar Eclipse
An eclipse of the moon takes place when the Earth crosses the Moon and the Sun, so blocking the Moon's shadow.
Position: Sun → Earth forces → Moon's location.
Types: Full & Partial Lunar Eclipses
In a lunar eclipse: The Moon seems red, which is sometimes known as a "Blood Moon."
|
Type of Eclipse |
Cause |
Visibility |
|
Solar Eclipse |
Moon blocks Sun’s light |
Observed from parts of the planet Earth |
|
Lunar Eclipse |
Earth’s shadow covers the Moon |
At Night Wherever You Are in the World |
Events concerning solar and lunar eclipses
-
Flashlight and global solar & lunar eclipse.
-
Observe the Moon during a lunar eclipse; write down its shape & color.
Interesting facts about shadows
-
A sundial allows you to keep time through shadows.
-
When the sun is rising or setting, the longest shadow exists.
-
Your shadow is the shortest at noon.
-
Like other animals, groundhogs rely on shadows to predict seasons — as on Groundhog Day.
-
There is no air to refract light on the Moon, so shadows are sharper.
Things you have learned!
- Opaque objects that block light create shadows.
- The direction of a shadow and its size are determined by the object's position & the light source.
- The rotation of the Earth also influences shadows, so day & night result from it.
- Ecliptical events are occasional occurrences of shadows in space.
CBSE Schools In Popular Cities
- CBSE Schools in Bangalore
- CBSE Schools in Mumbai
- CBSE Schools in Pune
- CBSE Schools in Hyderabad
- CBSE Schools in Chennai
- CBSE Schools in Gurgaon
- CBSE Schools in Kolkata
- CBSE Schools in Indore
- CBSE Schools in Sonipat
- CBSE Schools in Delhi
- CBSE Schools in Rohtak
- CBSE Schools in Bhopal
- CBSE Schools in Aurangabad
- CBSE Schools in Jabalpur
- CBSE Schools in Jaipur
- CBSE Schools in Jodhpur
- CBSE Schools in Nagpur
- CBSE Schools in Ahmednagar
- CBSE School In Tumkur














